Overview of Amazon Web Services (part 2)
To read part 1, please click here
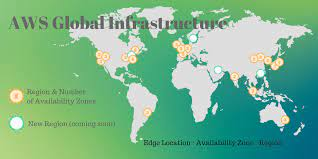
Global Infrastructure
In order to achieve higher fault tolerance and stability, each Amazon Region is designed to be completely isolated from the other Amazon Regions whereas Availability Zones are connected through low-latency links in a Region. Availability Zones are designed as an independent failure zone i.e. they are physically separated within a typical metropolitan region and are located in lower risk flood plains. Discrete Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) as well as onsite backup generation facilities are also provided by the independent substations along with the data centers situated in various Availability Zones, to reduce any risk of an event of the power grid impacting more than one Availability Zone.
Security & Compliance
Security
You can also get access to hundreds of tools as well as features by helping you to meet your security objectives by offering security-specific tools and features across network security, configuration management, access control, and data encryption. AWS environments are continuously audited with certifications from accreditation bodies across geographies and verticals where you can also take advantage of automated tools for asset inventory as well as privileged access reporting.
Benefits of AWS Security
- Keep your data safe- The AWS infrastructure keeps strong safeguards in place to help protect your privacy and all the data is stored in highly secure AWS data centers.
- Meet compliance requirements- AWS is capable of managing dozens of compliance programs in its infrastructure i.e. the segments of your compliance have already been completed.
- Save money- You can cut the costs with the help of AWS data centers by maintaining the highest standard of security without worrying about your own facility.
- Scale quickly- Security scales with your AWS Cloud usage. No matter the size of your business, the AWS infrastructure is designed to keep your data safe.
Compliance
The IT infrastructure that AWS offers to its customers is designed as well as managed in alignment with the best security practices and a variety of IT security standards and it also provides a wide range of information on its IT control environment whitepapers, reports, certifications, accreditations, and the other third-party attestations.
To read part 1, please click here



Comments
Post a Comment