Manage Insider Risk in Microsoft 365 (part 1)
For further details please click here
Insider Risk Management
The Insider Risk Management solution in the Microsoft 365 leverages the Microsoft Graph, security services, and connectors to Human Resources (HR) systems like SAP, to obtain real-time native signals such as file activity, communication sentiment, abnormal user behaviors, and resignation date. The built-in policy templates allows you to identify and mitigate the risky activities while simultaneously balancing the employee privacy versus organization risks with privacy-by-design architecture. Finally, the end-to-end integrated workflows ensures that the right people across security, HR, legal, and compliance are involved to quickly investigate and take action once a risk has been identified.
Risk Pain Points in the Modern Workplace
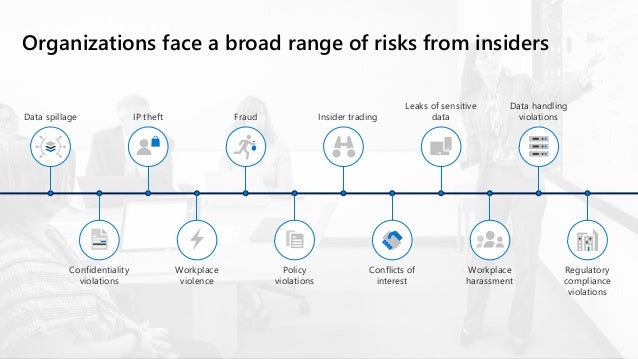
Managing and minimizing risks in your organization generally starts with understanding the types of the risks found in the modern workplace. Some examples of the internal risks from the employees includes:
- Intellectual Property (IP) theft
- Espionage
- Leaks of sensitive business assets
- Confidentiality violations
- Sabotage
- Fraud
- Insider trading
- Code-of-conduct violations
- Regulatory compliance violations
Insider risks vary by industry. In healthcare, internal fraud is the most frequently cited type of risk, while sabotage represents the greatest risk to the IT businesses.
Common Insider Risk Scenarios
- Data theft by departing employee- When employees leave an organization, either voluntarily or as the result of termination, there is often legitimate concerns that the company, customer, and employee data are at risk as the employees may either innocently assume that the particular project data isn't proprietary, or they may be tempted to take the company's data for personal gain and in violation of company policy as well as legal standards.
- Leak of sensitive or confidential information- In the most cases, employees try their best to properly handle sensitive or confidential information but occasionally they can make mistakes and the information is accidentally shared outside your organization or in violation of your information protection policies. Sometimes the employees may intentionally leak or share sensitive and confidential information with malicious intent as well as for potential personal gain.
- Actions and behaviors that violate corporate policies- Employee-to-employee communications are often a source of inadvertent or malicious violations of the corporate policies that can include offensive language, threats, and cyber-bullying between employees. This type of activity contributes to a hostile work environment and can result in the legal actions against both the employees and the larger organization.
Insider Risk Management Workflow
- Policies- Insider Risk Management policies determine which policies are in-scope and which types of the risk indicators are configured for alerts.
- Alerts- Insider Risk Management alerts are automatically generated by risk indicators defined in insider risk management policies while providing the compliance analysts and investigators an all-up view of the current risk status as well as allow your organization to triage and take actions for the discovered risks.
- Triage- Reviewers can quickly identify insider risk alerts and examine each to evaluate and triage. Alerts are resolved by opening a new case, assigning the alert to an existing case, or dismissing the alert.
- Investigate- Cases are manually created from alerts in the situations where further action is needed to address an issue for an employee.
- Action- After investigating the details of a case, you can easily take action by sending the employee a notice, resolving the case as benign, or escalating to a data or employee investigation.
For further details please click here





Comments
Post a Comment